IBM LAN server
IBMs LAN server is a relatively low-cost system that provides basic networking services. It is based on IBM’s OS/2 operating system. This allows the server to be run on the same machine as a workstation, similar to Netware server for OS/2.
Banyan VINES
VINES were introduced when Netware was still young. Although it has a catchier name than Netware (it is actually an acronym for virtual Networking system), Banyan’s product has always had a similar market. It is most often used in larger networks that span multiple locations.
One benefit of VINES is that it provides a directory service, similar to Netware NDS. For this and other reasons, VINES was the preferred enterprises network system for many companies. This was, after all, before Netware become available.
The directory service provided by VINES is called street talk. Now that Netware becoming prevalent in large networks, Banyan has introduced method of interesting street talk with Netware and other popular NOS software. Banyan’s recent focus has been on interesting VINES and street talk with the largest network of them all, the internet.
Peer-to-Peer Networking
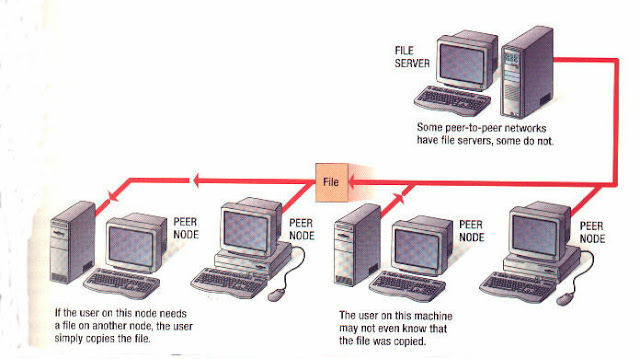
Some networks don’t use a server at all. These peer-to-peer networks allow each workstation to share its own files or printers. In a sense, each workstation acts as a server to provide accessed to its own disk drives and printers. Peer-to-peer networks are easy to set up and usually easier to maintain than a dedicated server. In addition, there’s no server to buy, so the price is lower.
Peer-to-peer networking isn’t the answer for all networks, however. Since the file and printer sharing are done in the back ground on workstations, the system can’t be a fast as a dedicated server and can’t handle nearly as many users. In addition, peer-to-peer systems usually lack the more advanced network services, such as messaging and directory services. Thus, peer-to-peer networks are best suited for smaller networks up to 20 users) or systems that require a minimum of resource sharing.
There are many peer-to-peer systems available from different companies. Here are a few.
- IBM OS/2 warp connect
- Microsoft windows for work group
- Artisoft LANtastic
- Apple talk
Peer-to-peer system can usually be used in combination with server-based networks such as Netware. This allows the best of both worlds: user can access files and printers on other user’s workstations when needed, and they can enjoy the benefits of a full-scale network server.
Review
The concept of networking has revolutionized the use of PCs in businesses. A network is a system that connects multiple computers allowing them to communicate with each other, share resources (files, printers, and so on) and communicate with mainframes and large networks.
Network components
A typical network consists of several components. The server run software called the network operating system (NOS), which allows it to act as a server.
Workstations are where the users of the network run applications. Workstations use the resources of the server. Each workstation has a network board (card), which interface that computer to the network.
Peripherals, such as tape backup drives, modems and printers, can be made available through the network and accessed by all users at workstation.
Finally a communications medium connects the machines. This is the actual network wiring.
Netware includes server software (the NOS) that you run on the server. In addition, client software is provided for a variety of clients. Netware also includes utilities that you can use to manage the network and its resources, you will run most of these utilities from a workstation, but some run on the server console.